Introduction to vitamin Dt
Vitamin D is called "sunshine vitamin" and contains vitamin D2 and vitamin D3. It is mainly derived from sunlight exposure and food intake of the skin. It is a neuroendocrine immune regulating hormone. It has a variety of biological effects, such as regulating calcium and phosphorus balance, promoting bone metabolism, and regulating immunity. It is an important fat soluble vitamin that participates in material metabolism, promotes growth and development, and maintains human health.
Based on the monitoring results of nutrition and health status of Chinese residents (2010-2013), the vitamin D deficiency rate of children aged 3-5 years was 8.9%. Studies have also found that 80% of pregnant women lack vitamin D, especially in the second and third trimester of pregnancy or when the skin absorbs less ultraviolet rays in winter; The nutritional status of vitamin D in middle-aged and elderly people is poor, 20% of them are insufficient, and 60% are in a state of deficiency.
Vitamin D plays an important role in all stages of life, especially in infants, pregnant women, the elderly and patients. Vitamin D deficiency is easy to induce various diseases, and excessive intake can lead to vitamin accumulation in the body and even poisoning. Therefore, paying attention to vitamin D monitoring and reasonable intervention and supplementation are beneficial to nutrition balance and health.
Clinical significance
(1) Accurately evaluate the nutritional status of vitamin D and formulate corresponding nutritional intervention programs.
(2) It is helpful to analyze the symptoms related to vitamin D nutritional imbalance and the causes and influencing factors of diseases.
(3) Determine the appropriate type of vitamin D supplement as the basis for adjusting the intervention program.
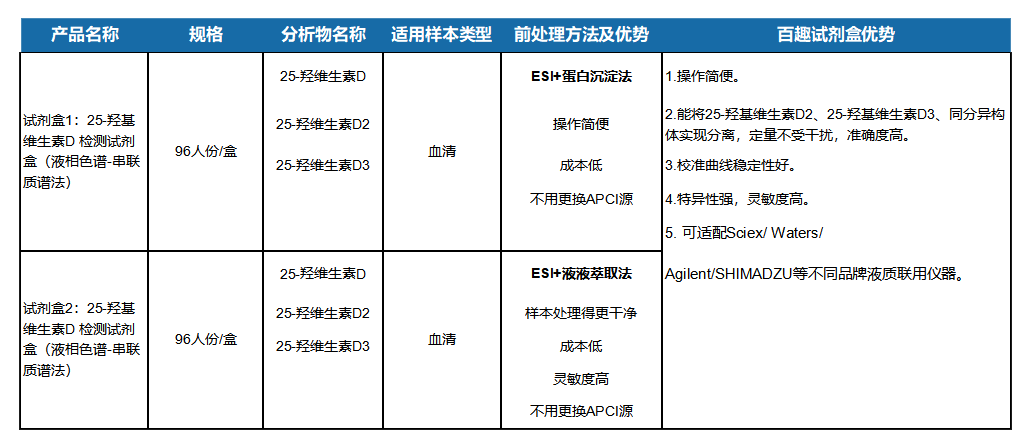
Characteristics of the kit and test indicators
Suitable population
Special groups | Pregnant and lactating women, the elderly with a history of falls and / or non traumatic fractures, people who lack sunshine (indoor work, night work, etc.), obese children and adults (BMI ≥ 30kg /m2), and people who receive weight reduction surgery. |
People with low immunity | Such as susceptible to colds, repeated respiratory tract infections and gastrointestinal tract discomfort. |
Sub healthy population | Physical weakness, malnutrition, fatigue, loss of appetite, sleep disorders, etc. |
Disease status population | Rickets, osteomalacia, osteoporosis, hyperparathyroidism, chronic kidney disease, liver failure, intestinal malabsorption syndrome, acute / chronic diarrhea, fatty diarrhea, pancreatic cystic fibrosis, inflammatory reactive bowel disease (Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis), radiation enteritis, lymphoma, granulomatous diseases, etc. |
People taking certain drugs | Antiepileptic drugs: phenytoin sodium, phenobarbital, etc; Glucocorticoids: prednisone, etc; Anti tuberculosis drugs: rifampicin equality; Azole antifungal drugs: ketoconazole, etc; Some lipid regulating drugs: colesene amine (cholesterimide), etc. |
Detect abnormal people | Monitor after intervention.,and recheck |

